- home
- Incheon Sejong Hospital
- Specialty Center
-
Endoscopy Center
- Health Improvement Center
- Endoscopy Center
- Internal medicine Center
- Surgery Center
- General Health Check-Up Center
- Emergency Medical Center
- Rehabilitation Center
- Spine-Joint Center
- Physiological Function Test Center
- Minimal Invasive Operation Center
- Dementia Special Center
- Infection Center
- Center for Bloodless Medicine and Surgery
- Breast and Thyroid Cancer Center
- Center for Precision Medicine
- Heart Transplantation Center
- Women’s Center
-
Health Improvement Center
Endoscopy Center
-
Internal medicine Center

Trusted center where specialists examine firsthand
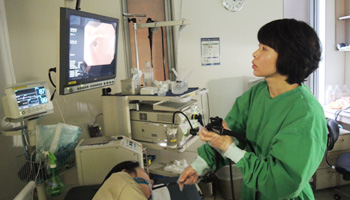
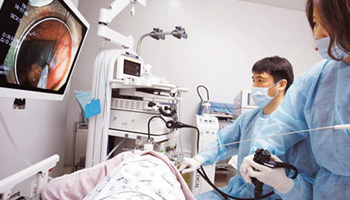
Our center makes it possible for an all-the-more precise and safe diagnosing and treatment with endoscopy specialists from prestigious universities taking examining to outcome consulting firsthand, sided with state-of-the-art equipments and specialized endoscopic examining rooms and sterilizer and disinfection kept to international standards.
We perform various diagnosis and procedures of different diseases via the endoscope, including ones with diagnostic purposes such as (sedated) gastroscopy, (unsedated) colonoscopy, cholangio-pancreatic endoscopy, and ones with therapeutic purposes such as polypectomy.
Endoscopy Center Procedures and Surgeries
| Upper Gastrointestinal endoscopy | Sedation and general examination via gastroscopy | Lower Gastrointestinal endoscopy- | Sedation and general examination via colonoscopy and rectosigmoidoscopy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Examination of Digestive Function | Esophageal manometry, rectal manometry, 24-Hour esophageal pH test | Examination of the Bronchus | Sedation and general examination via bronchoscopy |
| Therapeutic Endoscopy |
|
Additional tests during endoscopy |
|
Structure of Endoscopy Center
[Endoscopy Center] Lee, Mi Jung

- Education
-
- 2005 School of Medicine, Seonam University
- 2015 Master in Graduate School of Chosun University
- Background
-
- 2005 ~ 2006 Intern, The Catholic University of Korea Catholic Medical Center
- 2006 ~ 2010 Resident, The Catholic University of Korea Catholic Medical Center
- 2010 ~ 2012 Clinical Trainer, Gastroenterology, The Catholic University of Korea Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital
- 2012 ~ 2015 Dedicated to endoscopy of Health Improvement Center, The Catholic University of Korea Incheon St. Mary's Hospital
- 2017~ Present, Chief, Endoscopy Center, Mediplex Sejong Hostpital
Information Endoscopy
Gastroscopy
Take endoscopic examination when you have the following symptoms:
- frequent sour, burning feeling in stomach, common indigestion
- black-coloured stool or bright red hematochezia
- frequent abdominal pain after meals or sour taste in mouth (acid reflux)
- frequent gassy, bloated feeling
- dysphagia, chronic cough, burning feeling in chest
- a past history of stomach or esophageal cancer in the family
- a feeling of something stuck in the throat
- a history of chronic gastritis or ulcer in past endoscopy
Colonoscopy
Take endoscopic examination hen you have the following symptoms.
- apparent hematochezia
- a past history of polypectomy due to polyp found in colon
- frequent abdominal pain and gassy feeling
- receiving treatment for ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease
- severe constipation or long-term diarrhea
- inspection for colon and rectal cancer
- change in thickness of stool or number of bowel movement
- abnormal findings from colon study
- excessive weight loss, anorexia, fatigue
- unidentified anaemia
- a past history of colon diseases in family
Chromatoscopy
A test typically performed during a gastric or colonic endoscopy, by applying a specific coloring on the surface of the gastric or colon mucous membrane, for early diagnose of metaplasia in mucous membrane, intestinal metaplasia of stomach, early gastric cancer, early esophageal cancer and early colon cancer.
Therapeutic Endoscopy
Endoscopic procedures to treat lesions in mucous membrane, polyps and benign tumors
- Surgical procedures such as electrocoagulation, polypectomy, mucosal resection
- Endoscopic removal of foreign body (such as thorns, coins, etc) in the esophagus and stomach
- Hypertonic saline infusion or electrocoagulation of acute bleeding site in the mucous membrane of stomach and colon
- Endoscopic hemostatic therapy such as clipping
What is Esophageal Manometry?
This is a method of determining the function of sphincteral muscles in upper and lower esophagus, and peristaltic movement of esophageal corpus, to set a standard for diagnosing disorders in esophageal motility.
What is Rectal Manometry?
This is to evaluate the physiology of bowel movement which occurs through the function of internal and external anal sphincter muscles around the anal cavity.
24 hour PH test
This is to find out the exact condition and time of stomach acid regurgitation, in order to diagnose, by finding the relation between the reflux and symptoms.
Helicobacter pylori test
Endoscopic examining for helicobacter pylori, which are known to be related to gastritis, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, stomach cancer, chronic indigestion via a minute extraction of the mucosal membrane in the stomach.
Other than an endoscopic biopsy, methods like the urea breath test and serological tests are also commonly used.
Difference between Sedated and Unsedated Endoscopy
| General (Unsedated) Endoscopic Examination | Sedative (Sleep) Endoscopic Examination |
|---|---|
| A method of examination after performing basic procedures without using a sedative, in mutual cooperation between the patient and the staff, who will guide and explain through the process, all the while the patient being able to appeal their complaints on inconvenience and pain from delay in examining time due to their health condition and cleanliness of colon (in case of colonoscopy). | Sedative (sleep) gastroscopy is a method of infusing a type of drug in order to deteriorate consciousness and thus reduces uncomfortableness caused during the examination. However it is not an examination proceeded with the patient in an anesthetized condition but rather, a sedated state that is possible enough for just a certain level of cooperation from the patient. A sedative drug, as well as pain killer, is injected before proceeding with a sedative endoscopy, in order to reduce pain and uncomfortableness of patient. There may be side effects to this; complications such as dyspnea and hypoxia in the respiratory system, hypotension and palpitation in the cardiovascular system (0.1-0.54%) and rarely lead to death (0.03%), sometimes requiring an emergency care due to hypersensiticity. Extra caution is required for sedative endoscopy if the patient is already with repiratory disorders, pulmonary dysfunction, kidney disorders and cardiac disorders and will be required to sign an uninsured agreement about parts that are not covered by the health insurance. Resting is needed after and endoscopy; no driving should be done for the rest of the day after an endoscopic examination and important meetings and work affairs should be avoided. A guardian must accompany the patient, for danger prevention suh as falls. |



